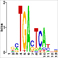
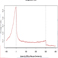
Chromatin Regulator | Alias |
| HDAC6 | HD6; JM21; FLJ16239 |
External Links: | Wiki GeneCards NCBI UniProt |
Related histone modifications: | H2AK5ac;H3K4ac;H3K14ac;H3K27ac;H3K56ac;H4K5ac;H4K8ac;H4K12ac;H4K16ac |
Introduction | |
| Full Name: Histone deacetylase 6
.
HDAC6 is a unique deacetylase belonging to the class IIb HDACs. It contains two catalytic domains and a zinc finger (ZnF) motif. It is a critical component of stress granules (SGs) and is involved in cellular stress responses, neurodegenerative disorders, α-tubulin acetylation, and ubiquitination signaling pathways (1-14).
|
Function and Interaction | |
| HDAC6 is a unique deacetylase belonging to the class IIb HDACs. It contains two catalytic domains and a zinc finger (ZnF) motif. It is a critical component of stress granules (SGs) and is involved in cellular stress responses, neurodegenerative disorders, α-tubulin acetylation, and ubiquitination signaling pathways (1-14).
|
Disease Association | |
| HDAC6 overexpression can result in increased invasion in breast cancer cells (10). Additionally, the catalytic activity of HDAC6 can be enhanced when the pressure of the left ventricular (LV) or right ventricular (RV) side is overloaded, which is increased by G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR) signaling in myocytes and cytokine receptor signaling in fibroblasts, suggesting an association with cardiovascular disease (11). HDAC6 plays a role in neuropathies, and inhibition of HDAC6 can enhance the level of α-tubulin acetylation, supplementing the axonal loss observed in HSPB1 (27 kDa small heat-shock protein gene)-related Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease (CMT) (9). HDAC6 is capable of regulating estrogen receptor (ER) α in uterine leiomyomata cells, indicating it as a therapeutic target for leiomyoma treatment (12). HDAC6 is also related to some neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer, Parkinson, and Huntington diseases (7).
|
ChIP-Seq data
ChIP-Seq data of related histone modifications
|
| Notice: For bigwiggle or bed file download, if the browser cannot automatically download the file,
users can right click the hyperlink and then click the "Save link as..." button, which will automatically redirect to download dialogue box, or click the "Copy link address" button
and access the website in a new tab page. For data analysis in Cistrome, users should first login into the Cistrome website,
then press the "Send Bed" or "Send Big wiggle" button. For data download by Cistrome, users can follow this tutorial.
|
References | |
1. Legros, S., Boxus, M., Gatot, J.S., Van Lint, C., Kruys, V., Kettmann, R., Twizere, J.C. and Dequiedt, F. (2011) The HTLV-1 Tax protein inhibits formation of stress granules by interacting with histone deacetylase 6. Oncogene, 30, 4050-4062.
2. Bali, P., Pranpat, M., Bradner, J., Balasis, M., Fiskus, W., Guo, F., Rocha, K., Kumaraswamy, S., Boyapalle, S., Atadja, P. et al. (2005) Inhibition of histone deacetylase 6 acetylates and disrupts the chaperone function of heat shock protein 90: a novel basis for antileukemia activity of histone deacetylase inhibitors. J Biol Chem, 280, 26729-26734.
3. Kovacs, J.J., Murphy, P.J., Gaillard, S., Zhao, X., Wu, J.T., Nicchitta, C.V., Yoshida, M., Toft, D.O., Pratt, W.B. and Yao, T.P. (2005) HDAC6 regulates Hsp90 acetylation and chaperone-dependent activation of glucocorticoid receptor. Mol Cell, 18, 601-607.
4. Matsuyama, A., Shimazu, T., Sumida, Y., Saito, A., Yoshimatsu, Y., Seigneurin-Berny, D., Osada, H., Komatsu, Y., Nishino, N., Khochbin, S. et al. (2002) In vivo destabilization of dynamic microtubules by HDAC6-mediated deacetylation. EMBO J, 21, 6820-6831.
5. Hubbert, C., Guardiola, A., Shao, R., Kawaguchi, Y., Ito, A., Nixon, A., Yoshida, M., Wang, X.F. and Yao, T.P. (2002) HDAC6 is a microtubule-associated deacetylase. Nature, 417, 455-458.
6. Zhang, Y., Li, N., Caron, C., Matthias, G., Hess, D., Khochbin, S. and Matthias, P. (2003) HDAC-6 interacts with and deacetylates tubulin and microtubules in vivo. Embo Journal, 22, 1168-1179.
7. Li, G.Y., Jiang, H.Y., Chang, M., Xie, H.R. and Hu, L.S. (2011) HDAC6 alpha-tubulin deacetylase: A potential therapeutic target in neurodegenerative diseases. J Neurol Sci, 304, 1-8.
8. Iwata, A., Riley, B.E., Johnston, J.A. and Kopito, R.R. (2005) HDAC6 and microtubules are required for autophagic degradation of aggregated Huntingtin. J Biol Chem, 280, 40282-40292.
9. d'Ydewalle, C., Krishnan, J., Chiheb, D.M., Van Damme, P., Irobi, J., Kozikowski, A.P., Vanden Berghe, P., Timmerman, V., Robberecht, W. and Van Den Bosch, L. (2011) HDAC6 inhibitors reverse axonal loss in a mouse model of mutant HSPB1-induced Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease. Nat Med, 17, 968-U986.
10. Park, S.Y., Jun, J.A., Jeong, K.T., Heo, H.J., Sohn, J.S., Lee, H.Y., Park, C.G. and Kang, J. (2011) Histone deacetylases 1, 6 and 8 are critical for invasion in breast cancer. Oncol Rep, 25, 1677-1681.
11. Lemon, D.D., Horn, T.R., Cavasin, M.A., Jeong, M.Y., Haubold, K.W., Long, C.S., Irwin, D.C., McCune, S.A., Chung, E., Leinwand, L.A. et al. (2011) Cardiac HDAC6 catalytic activity is induced in response to chronic hypertension. J Mol Cell Cardiol, 51, 41-50.
12. Wei, L.H., Torng, P.L., Hsiao, S.M., Jeng, Y.M., Chen, M.W. and Chen, C.A. (2011) Histone Deacetylase 6 Regulates Estrogen Receptor alpha in Uterine Leiomyoma. Reprod Sci, 18, 755-762.
13. Gregoretti, I.V., Lee, Y.M. and Goodson, H.V. (2004) Molecular evolution of the histone deacetylase family: Functional implications of phylogenetic analysis. J Mol Biol, 338, 17-31.
14. Kwon, S., Zhang, Y. and Matthias, P. (2007) The deacetylase HDAC6 is a novel critical component of stress granules involved in the stress response. Gene Dev, 21, 3381-3394.
|