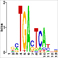
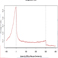
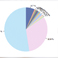
Chromatin Regulator | Alias |
| SMARCA4 | BRG1; SNF2; SWI2; MRD16; RTPS2; BAF190; SNF2L4; SNF2LB; hSNF2b; BAF190A |
External Links: | Wiki GeneCards NCBI UniProt |
Related histone modifications: | NA
|
Introduction | |
| Full Name: SWI/SNF-related, matrix-associated, actin-dependent regulator of chromatin, subfamily a, member 4
.
SMARCA4 is one of the catalytic subunits of the ATP-dependent SWI/SNF (SWItch/Sucrose NonFermentable)-like chromatin-remodeling complex. Mutations in SMARCA4 can result in embryonic lethality during the peri-implantation stage, and this protein was identified as the first chromatin-modifying factor essential for beta-globin modulation. It is indispensable for normal levels of 5-hydroxy-methylcytosine (5hmC) in vivo and is involved in erythropoiesis and organogenesis, T cell development, vascular development, heart development, limb patterning, skin barrier formation, and gastrointestinal smooth muscle development (1-17).
|
Function and Interaction | |
| Deletion of SMARCA4 in the T cell lineage can lead to certain abnormalities, including activation of CD4 during the double-negative (DN; CD4-CD8-) stage and a block during the transition from the DN stage to the double-positive (CD4+CD8+) stage. Although mutations in SMARCA4 in mature T cells at the periphery can lead to escape from the block stage, they can result in a smaller T cell populations, which affects the immune capacity and health of mice (1). SMARCA4 interacts with histone deacetylase (HDAC) and poly (ADP ribose) polymerase (PARP), controls the expression of Bmp10, and suppresses p57kip2, thus participating in cardiac growth and differentiation (2). SMARCA4 is required for normal vascular development, as SMARCA4 knockout in embryonic blood vessels can lead to yolk sac vascular remodeling defects, partly through disruption of the Wnt signaling pathway (3-4). SMARCA4 is reportedly capable of modulating both Wnt receptor genes and Wnt target genes, and of deletion SMARCA4 can reduce Wnt signaling in endothelial cells and suppress some Wnt receptors belonging to the frizzled family as well as β-catenin degradation (4). CHD4 plays an opposite role to that of SMARCA4 in controlling the vascular Wnt signaling pathway (5). SMARCA4 is believed to bind distal GATA1-bound sites during differentiation and generate a longer nucleosome linker region around the GATA1 sites by shifting nucleosomes away, thus mediating the binding of TAL1 and being associated with subsequent transcriptional activation (6). SMARCA4 is also essential for IFN-γ-stimulated TRIM22 expression in an IRF-1-dependent fashion (7).
|
Disease Association | |
| SMARCA4 is activated in some hypertrophic cardiomyopathy patients. SMARCA4 levels are related to changes in myosin heavy chain (MHC) levels and disease survival (2). SMARCA4 is also related to intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms (IPMN) of the pancreas (8).
|
ChIP-Seq data
| Species | Cell line | Cell type | Tissue | Data | Download | Send to Cistrome | Analysis Figures | Comparison | Reference |
|---|
| Mus musculus | None | Embryonic Stem Cell | None | GSE58408 ,GSM1572678 |
|
Click Download | NA | NA |
|
| Notice: For bigwiggle or bed file download, if the browser cannot automatically download the file,
users can right click the hyperlink and then click the "Save link as..." button, which will automatically redirect to download dialogue box, or click the "Copy link address" button
and access the website in a new tab page. For data analysis in Cistrome, users should first login into the Cistrome website,
then press the "Send Bed" or "Send Big wiggle" button. For data download by Cistrome, users can follow this tutorial.
|
References | |
1. Gebuhr, T.C., Kovalev, G.I., Bultman, S., Godfrey, V., Su, L.S. and Magnuson, T. (2003) The role of Brg1, a catalytic subunit of mammalian chromatin-remodeling complexes, in T cell development. J Exp Med, 198, 1937-1949.
2. Hang, C.T., Yang, J., Han, P., Cheng, H.L., Shang, C., Ashley, E., Zhou, B. and Chang, C.P. (2010) Chromatin regulation by Brg1 underlies heart muscle development and disease. Nature, 466, 62-U74.
3. Griffin, C.T., Brennan, J. and Magnuson, T. (2008) The chromatin-remodeling enzyme BRG1 plays an essential role in primitive erythropoiesis and vascular development. Development, 135, 493-500.
4. Griffin, C.T., Curtis, C.D., Davis, R.B., Muthukumar, V. and Magnuson, T. (2011) The chromatin-remodeling enzyme BRG1 modulates vascular Wnt signaling at two levels. P Natl Acad Sci USA, 108, 2282-2287.
5. Curtis, C.D. and Griffin, C.T. (2012) The Chromatin-Remodeling Enzymes BRG1 and CHD4 Antagonistically Regulate Vascular Wnt Signaling. Mol Cell Biol, 32, 1312-1320.
6. Hu, G.Q., Schones, D.E., Cui, K.R., Ybarra, R., Northrup, D., Tang, Q.S., Gattinoni, L., Restifo, N.P., Huang, S.M. and Zhao, K.J. (2011) Regulation of nucleosome landscape and transcription factor targeting at tissue-specific enhancers by BRG1. Genome Res, 21, 1650-1658.
7. Wang, Y.X., Gao, B., Xu, W. and Xiong, S.D. (2011) BRG1 is indispensable for IFN-gamma-induced TRIM22 expression, which is dependent on the recruitment of IRF-1. Biochem Bioph Res Co, 410, 549-554.
8. Dal Molin, M., Hong, S.M., Hebbar, S., Sharma, R., Scrimieri, F., de Wilde, R.F., Mayo, S.C., Goggins, M., Wolfgang, C.L., Schulick, R.D. et al. (2012) Loss of expression of the SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling subunit BRG1/SMARCA4 is frequently observed in intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas. Hum Pathol, 43, 585-591.
9. Khavari, P.A., Peterson, C.L., Tamkun, J.W., Mendel, D.B. and Crabtree, G.R. (1993) BRG1 contains a conserved domain of the SWI2/SNF2 family necessary for normal mitotic growth and transcription. Nature, 366, 170-174.
10. Randazzo, F.M., Khavari, P., Crabtree, G., Tamkun, J. and Rossant, J. (1994) Brg1 - a Putative Murine Homolog of the Drosophila-Brahma Gene, a Homeotic Gene Regulator. Developmental Biology, 161, 229-242.
11. Bultman, S., Gebuhr, T., Yee, D., La Mantia, C., Nicholson, J., Gilliam, A., Randazzo, F., Metzger, D., Chambon, P., Crabtree, G. et al. (2000) A Brg1 null mutation in the mouse reveals functional differences among mammalian SWI/SNF complexes. Mol Cell, 6, 1287-1295.
12. Bultman, S.J., Gebuhr, T.C. and Magnuson, T. (2005) A Brg1 mutation that uncouples ATPase activity from chromatin remodeling reveals an essential role for SWI/SNF-related complexes in beta-globin expression and erythroid development. Gene Dev, 19, 2849-2861.
13. Stankunas, K., Hang, C.T., Tsun, Z.Y., Chen, H., Lee, N.V., Wu, J.I., Shang, C., Bayle, J.H., Shou, W., Iruela-Arispe, M.L. et al. (2008) Endocardial Brg1 represses ADAMTS1 to maintain the microenvironment for myocardial morphogenesis. Dev Cell, 14, 298-311.
14. Takeuchi, J.K., Lou, X., Alexander, J.M., Sugizaki, H., Delgado-Olguin, P., Holloway, A.K., Mori, A.D., Wylie, J.N., Munson, C., Zhu, Y.H. et al. (2011) Chromatin remodelling complex dosage modulates transcription factor function in heart development. Nat Commun, 2.
15. Indra, A.K., Dupe, V., Bornert, J.M., Messaddeq, N., Yaniv, M., Mark, M., Chambon, P. and Metzger, D. (2005) Temporally controlled targeted somatic mutagenesis in embryonic surface ectoderm and fetal epidermal keratinocytes unveils two distinct developmental functions of BRG1 in limb morphogenesis and skin barrier formation. Development, 132, 4533-4544.
16. Zhang, M., Chen, M., Kim, J.R., Zhou, J.L., Jones, R.E., Tune, J.D., Kassab, G.S., Metzger, D., Ahlfeld, S., Conway, S.J. et al. (2011) SWI/SNF Complexes Containing Brahma or Brahma-Related Gene 1 Play Distinct Roles in Smooth Muscle Development. Mol Cell Biol, 31, 2618-2631.
17. Yildirim, O., Li, R.W., Hung, J.H., Chen, P.B., Dong, X.J., Ee, L.S., Weng, Z.P., Rando, O.J. and Fazzio, T.G. (2011) Mbd3/NURD Complex Regulates Expression of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Marked Genes in Embryonic Stem Cells. Cell, 147, 1498-1510.
|