Chromatin Regulator | Alias |
| KDM5C | MRXJ; SMCX; MRXSJ; XE169; MRXSCJ; JARID1C; DXS1272E |
External Links: | Wiki GeneCards NCBI UniProt |
Related histone modifications: | H3K4me3;H3K4me2 |
Introduction | |
| Full Name: Lysine (K)-specific demethylase 5C
.
KDM5C is a member of the highly conserved ARID protein family and was first recognized as an X-chromosome gene that escapes X-inactivation in both mice and humans. It contains a JmjN domain, an ARID domain, a JmjC domain, a C5HC2 zinc finger domain, and a PHD zinc finger domain. KDM5C expression may be tissue- and developmental stage-specific, and it is associated with transcriptional repression and chromatin remodeling, playing a role in normal brain development and function, tumorigenesis, development, cell growth, and differentiation (1-13).
|
Function and Interaction | |
| KDM5C forms a complex with HDAC1, HDAC2, G9a, and REST. REST and KDM5C have been shown to co-bind the promoter regions of some REST target genes, indicating the involvement of KDM5C in chromatin dynamics and REST-related repression (2). KDM5C is also associated with Smad3, an intracellular mediator of transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β), and acting as a corepressor of Smad3. Hence, KDM5C may be involved in tumorigenesis via interfering with the tumor-suppressing activity of the TGF-b/ Smad3 signaling pathway (3).
|
Disease Association | |
| Mutations in KDM5C are related to X-linked mental retardation (XLMR) and epilepsy (4-5). One study also associated a mutation in KDM5C with a patient with autism spectrum disorder (6). This novel mutation in KDM5C can result in intellectual disability, short stature, speech delay, hyperactivity, violent behavior, and a high palate (8). KDM5Cs are suggested to act as tumor enhancers in clear-cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) (7).
|
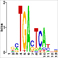
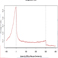
ChIP-Seq data
ChIP-Seq data of related histone modifications
| Products/Substrates | Species | Cell line | Cell type | Tissue | Data | Download |
Send to Cistrome | Analysis Figures | Reference |
|---|
| H3K4me3 |
Mus musculus |
V6.5 |
Embryonic Stem Cell |
Embryo |
GSE48172 ,GSM1171628 |
Bed
Big wiggle |
|
Click Download | 23934151 | | H3K4me3 |
Mus musculus |
V6.5 |
Embryonic Stem Cell |
Embryo |
GSE48172 ,GSM1171630 |
Bed
Big wiggle |
|
Click Download | 23934151 | | H3K4me3 |
Mus musculus |
V6.5 |
Embryonic Stem Cell |
Embryo |
GSE48172 ,GSM1171632 |
Bed
Big wiggle |
|
Click Download | 23934151 | | H3K4me3 |
Mus musculus |
E14 |
Embryonic Stem Cell |
Embryo |
GSE52071 ,GSM1258237 |
Bed
Big wiggle |
|
Click Download | 24423662 | | H3K4me3 |
Mus musculus |
NA |
Embryonic Stem Cell |
Embryo |
GSE52071 ,GSM1276704 |
Bed
Big wiggle |
|
Click Download | 24423662 | | H3K4me3 |
Mus musculus |
E14 |
Embryonic Stem Cell |
Embryo |
GSE52071 ,GSM1276705 |
Bed
Big wiggle |
|
Click Download | 24423662 | | H3K4me3 |
Mus musculus |
R1 |
Embryonic Stem Cell |
Embryo |
GSE53087 ,GSM1282137 |
Bed
Big wiggle |
|
Click Download | 24495580 | | H3K4me3 |
Mus musculus |
R1 |
Embryonic Stem Cell |
Embryo |
GSE53087 ,GSM1282139 |
Bed
Big wiggle |
|
Click Download | 24495580 | | H3K4me3 |
Homo sapiens |
caki-1 |
None |
Kidney |
GSE73267 ,GSM1889909 |
Bed
Big wiggle |
|
Click Download | 26551685 | | H3K4me3 |
Homo sapiens |
caki-1 |
None |
Kidney |
GSE73267 ,GSM1889910 |
Bed
Big wiggle |
|
Click Download | 26551685 | | H3K4me3 |
Mus musculus |
XT67E1 |
Embryonic Stem Cell |
Embryo |
GSE15884 ,GSM397402 |
Bed
Big wiggle |
|
Click Download | 19581487 | | H3K4me3 |
Mus musculus |
XT67E1 |
Embryonic Stem Cell |
Embryo |
GSE15884 ,GSM397403 |
Bed
Big wiggle |
|
Click Download | 19581487 | | H3K4me3 |
Mus musculus |
XT67E1 |
Embryonic Stem Cell |
Embryo |
GSE15884 ,GSM397404 |
Bed
Big wiggle |
|
Click Download | 19581487 | | H3K4me3 |
Mus musculus |
C6 |
Embryonic Stem Cell |
Embryo |
GSE16893 ,GSM487545 |
Bed
Big wiggle |
|
Click Download | 20211137 | | H3K4me3 |
Mus musculus |
C6 |
Embryonic Stem Cell |
Embryo |
GSE16893 ,GSM487548 |
Bed
Big wiggle |
|
Click Download | 20211137 | | H3K4me3 |
Mus musculus |
TNGA |
Embryonic Stem Cell |
Embryo |
GSE23943 ,GSM590110 |
Bed
Big wiggle |
|
Click Download | 22541430 | | H3K4me3 |
Homo sapiens |
K562 |
Erythroblast |
Bone Marrow |
GSE28162 ,GSM608165 |
Bed
Big wiggle |
|
Click Download | 21596310 | | H3K4me3 |
Mus musculus |
E14 |
Embryonic Stem Cell |
Embryo |
GSE26136 ,GSM651193 |
Bed
Big wiggle |
|
Click Download | 21335234 | | H3K4me3 |
Mus musculus |
CMTi-1 |
Embryonic Stem Cell |
Embryo |
GSE34483 ,GSM849941 |
Bed
Big wiggle |
|
Click Download | 23260488 | | H3K4me3 |
Homo sapiens |
K562 |
Erythroblast |
Bone Marrow |
GSE35294 ,GSM865280 |
Bed
Big wiggle |
|
Click Download | 23754963 | | H3K4me3 |
Homo sapiens |
K562 |
Erythroblast |
Bone Marrow |
GSE35294 ,GSM865281 |
Bed
Big wiggle |
|
Click Download | 23754963 | | H3K4me3 |
Mus musculus |
R1 |
Embryonic Stem Cell |
Embryo |
GSE36294 ,GSM886518 |
Bed
Big wiggle |
|
Click Download | 24381111 | | H3K4me3 |
Mus musculus |
TC1 |
Embryonic Stem Cell |
Embryo |
GSE37776 ,GSM928131 |
Bed
Big wiggle |
|
Click Download | 22666422 | | H3K4me3 |
Mus musculus |
3.2N |
Embryonic Stem Cell |
Embryo |
GSE37776 ,GSM928132 |
Bed
Big wiggle |
|
Click Download | 22666422 | | H3K4me3 |
Mus musculus |
NA |
Embryonic Stem Cell |
Embryo |
GSE39472 ,GSM969829 |
Bed
Big wiggle |
|
Click Download | 22826230 | | H3K4me3 |
Mus musculus |
NA |
Embryonic Stem Cell |
Embryo |
GSE39472 ,GSM969830 |
Bed
Big wiggle |
|
Click Download | 22826230 | | H3K4me3 |
Mus musculus |
E36 |
Embryonic Stem Cell |
Embryo |
GSE39496 ,GSM970227 |
Bed
Big wiggle |
|
Click Download | 24289921 | | H3K4me3 |
Mus musculus |
E36 |
Embryonic Stem Cell |
Embryo |
GSE39496 ,GSM970228 |
Bed
Big wiggle |
|
Click Download | 24289921 |
|
| Notice: For bigwiggle or bed file download, if the browser cannot automatically download the file,
users can right click the hyperlink and then click the "Save link as..." button, which will automatically redirect to download dialogue box, or click the "Copy link address" button
and access the website in a new tab page. For data analysis in Cistrome, users should first login into the Cistrome website,
then press the "Send Bed" or "Send Big wiggle" button. For data download by Cistrome, users can follow this tutorial.
|
References | |
1. Iwase, S., Lan, F., Bayliss, P., de la Torre-Ubieta, L., Huarte, M., Qi, H.H., Whetstine, J.R., Bonni, A., Roberts, T.M. and Shi, Y. (2007) The X-linked mental retardation gene SMCX/JARID1C defines a family of histone H3 lysine 4 demethylases. Cell, 128, 1077-1088.
2. Tahiliani, M., Mei, P., Fang, R., Leonor, T., Rutenberg, M., Shimizu, F., Li, J., Rao, A. and Shi, Y. (2007) The histone H3K4 demethylase SMCX links REST target genes to X-linked mental retardation. Nature, 447, 601-605.
3. Kim, T.D., Shin, S. and Janknecht, R. (2008) Repression of Smad3 activity by histone demethylase SMCX/JARID1C. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 366, 563-567.
4. Jensen, L.R., Amende, M., Gurok, U., Moser, B., Gimmel, V., Tzschach, A., Janecke, A.R., Tariverdian, G., Chelly, J., Fryns, J.P. et al. (2005) Mutations in the JARID1C gene, which is involved in transcriptional regulation and chromatin remodeling, cause X-linked mental retardation. Am J Hum Genet, 76, 227-236.
5. Tzschach, A., Lenzner, S., Moser, B., Reinhardt, R., Chelly, J., Fryns, J.P., Kleefstra, T., Raynaud, M., Turner, G., Ropers, H.H. et al. (2006) Novel JARID1C/SMCX Mutations in Patients With Xlinked Mental Retardation. Hum Mutat, 27, 389-390.
6. Adegbola, A., Gao, H.L., Sommer, S. and Browning, M. (2008) A novel mutation in JARID1C/SMCX in a patient with autism spectrum disorder (ASD). Am J Med Genet A, 146A, 505-511.
7. Niu, X., Zhang, T., Liao, L., Zhou, L., Lindner, D.J., Zhou, M., Rini, B., Yan, Q. and Yang, H. (2012) The von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor protein regulates gene expression and tumor growth through histone demethylase JARID1C. Oncogene, 31, 776-786.
8. Santos-Reboucas, C.B., Fintelman-Rodrigues, N., Jensen, L.R., Kuss, A.W., Ribeiro, M.G., Campos, M., Santos, J.M. and Pimentel, M.M.G. (2011) A novel nonsense mutation in KDM5C/JARID1C gene causing intellectual disability, short stature and speech delay. Neurosci Lett, 498, 67-71.
9. Yi, L., Hao, Z., Yang, T., Wang, S., Xing, B. and Xu, Y. (2007) cDNA cloning, bioinformatic and tissue-specific expression analysis of porcine JARID1C gene. J Genet Genomics, 34, 1088-1096.
10. Agulnik, A.I., Mitchell, M.J., Mattei, M.G., Borsani, G., Avner, P.A., Lerner, J.L. and Bishop, C.E. (1994) A novel X gene with a widely transcribed Y-linked homologue escapes X-inactivation in mouse and human. Hum Mol Genet, 3, 879-884.
11. Wu, J., Salido, E.C., Yen, P.H., Mohandas, T.K., Heng, H.H., Tsui, L.C., Park, J., Chapman, V.M. and Shapiro, L.J. (1994) The murine Xe169 gene escapes X-inactivation like its human homologue. Nat Genet, 7, 491-496.
12. Li, N. and Carrel, L. (2008) Escape from X chromosome inactivation is an intrinsic property of the Jarid1c locus. P Natl Acad Sci USA, 105, 17055-17060.
13. Xu, J., Deng, X.X. and Disteche, C.M. (2008) Sex-Specific Expression of the X-Linked Histone Demethylase Gene Jarid1c in Brain. PLoS One, 3.
|