Chromatin Regulator | Alias |
| SIRT1 | SIR2L1 |
External Links: | Wiki GeneCards NCBI UniProt |
Related histone modifications: | H4K16ac;H1K25ac;H3K9ac |
Introduction | |
| Full Name: Sirtuin 1
.
SIRT1 is a nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+)-dependent protein deacetylase belonging to the sirtuin family (class III HDAC). It exhibits both histone and non-histone substrates, and it participates in glucose metabolism, stress responses, DNA repair, the cell cycle, apoptosis, aging, cancer, differentiation and development (1-7).
|
Function and Interaction | |
| SIRT1 is recruited to chromatin by transcription factors and then carries out its deacetylation function to repress gene transcription (8). SIRT1 interacts with ZEB1, which is an epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT)-inducing transcription factor, thus regulating the EMT process (9). P53 is a well-known tumor repressor and acts as a non-histone substrate of SIRT1. SIRT1 inhibition can result in an increase in P53 acetylation and promotion of its transcriptional activity in CML (chronic myelogenous leukemia) progenitors, thereby decreasing the number of CML leukemia stem cells (10-11). SIRT1 is capable of maintaining the identity of hematopoietic stem cells through ROS and p53 repression and FOXO activation, and deletion of SIRT1 can lead to the formation of cholesterol gallstones (12-13). SIRT1 overexpression reduces the level of acetylation on the NF-κBas p65 subunit, decreasing cisplatin-induced cytotoxicity and suggesting this factor as a potential pharmaceutical target for the treatment of inflammatory injuries (14).
|
Disease Association | |
| SIRT1 is a potential candidate for targeting in prostate cancer treatment, as its overexpression can reverse EMT and prevent the growth of prostate cancer cells (9). Furthermore, SIRT1 overexpression can decrease cell proliferation and tumor formation in colon cancer, and SIRT1 is also overexpressed in CML cells (11,15).
|
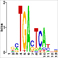
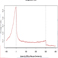
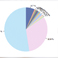
ChIP-Seq data
ChIP-Seq data of related histone modifications
|
| Notice: For bigwiggle or bed file download, if the browser cannot automatically download the file,
users can right click the hyperlink and then click the "Save link as..." button, which will automatically redirect to download dialogue box, or click the "Copy link address" button
and access the website in a new tab page. For data analysis in Cistrome, users should first login into the Cistrome website,
then press the "Send Bed" or "Send Big wiggle" button. For data download by Cistrome, users can follow this tutorial.
|
References | |
1. Fulco, M., Cen, Y., Zhao, P., Hoffman, E.P., McBurney, M.W., Sauve, A.A. and Sartorelli, V. (2008) Glucose restriction inhibits skeletal myoblast differentiation by activating SIRT1 through AMPK-mediated regulation of Nampt. Dev Cell, 14, 661-673.
2. Luo, J.Y., Nikolaev, A.Y., Imai, S., Chen, D.L., Su, F., Shiloh, A., Guarente, L. and Gu, W. (2001) Negative control of p53 by Sir2 alpha promotes cell survival under stress. Cell, 107, 137-148.
3. Bordone, L. and Guarente, L. (2005) Calorie restriction, SIRT1 and metabolism: Understanding longevity. Nat Rev Mol Cell Bio, 6, 298-305.
4. Cheng, H.L., Mostoslavsky, R., Saito, S., Manis, J.P., Gu, Y.S., Patel, P., Bronson, R., Appella, E., Alt, F.W. and Chua, K.F. (2003) Developmental defects and p53 hyperacetylation in Sir2 homolog (SIRT1)-deficient mice. P Natl Acad Sci USA, 100, 10794-10799.
5. Liu, T., Liu, P.Y. and Marshall, G.M. (2009) The Critical Role of the Class III Histone Deacetylase SIRT1 in Cancer. Cancer Res, 69, 1702-1705.
6. Kim, E.J. and Um, S.J. (2008) SIRT1: roles in aging and cancer. Bmb Rep, 41, 751-756.
7. Picard, F., Kurtev, M., Chung, N., Topark-Ngarm, A., Senawong, T., de Oliveira, R.M., Leid, M., McBurney, M.W. and Guarente, L. (2004) Sirt1 promotes fat mobilization in white adipocytes by repressing PPAR-gamma (vol 429, pg 771, 2004). Nature, 430, 921-921.
8. Dai, Y. and Faller, D.V. (2008) Transcription Regulation by Class III Histone Deacetylases (HDACs)-Sirtuins. Transl Oncogenomics, 3, 53-65.
9. Byles, V., Zhu, L., Lovaas, J.D., Chmilewski, L.K., Wang, J., Faller, D.V. and Dai, Y. (2012) SIRT1 induces EMT by cooperating with EMT transcription factors and enhances prostate cancer cell migration and metastasis. Oncogene, 31, 4619-4629.
10. Brooks, C.L. and Gu, W. (2011) The impact of acetylation and deacetylation on the p53 pathway. Protein Cell, 2, 456-462.
11. Li, L., Wang, L., Wang, Z., Ho, Y., McDonald, T., Holyoake, T.L., Chen, W. and Bhatia, R. (2012) Activation of p53 by SIRT1 inhibition enhances elimination of CML leukemia stem cells in combination with imatinib. Cancer Cell, 21, 266-281.
12. Matsui, K., Ezoe, S., Oritani, K., Shibata, M., Tokunaga, M., Fujita, N., Tanimura, A., Sudo, T., Tanaka, H., McBurney, M.W. et al. (2012) NAD-dependent histone deacetylase, SIRT1, plays essential roles in the maintenance of hematopoietic stem cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 418, 811-817.
13. Purushotham, A., Xu, Q., Lu, J., Foley, J.F., Yan, X., Kim, D.H., Kemper, J.K. and Li, X. (2012) Hepatic deletion of SIRT1 decreases hepatocyte nuclear factor 1alpha/farnesoid X receptor signaling and induces formation of cholesterol gallstones in mice. Mol Cell Biol, 32, 1226-1236.
14. Jung, Y.J., Lee, J.E., Lee, A.S., Kang, K.P., Lee, S., Park, S.K., Lee, S.Y., Han, M.K., Kim, D.H. and Kim, W. (2012) SIRT1 overexpression decreases cisplatin-induced acetylation of NF-kappaB p65 subunit and cytotoxicity in renal proximal tubule cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 419, 206-210.
15. Firestein, R., Blander, G., Michan, S., Oberdoerffer, P., Ogino, S., Campbell, J., Bhimavarapu, A., Luikenhuis, S., de Cabo, R., Fuchs, C. et al. (2008) The SIRT1 deacetylase suppresses intestinal tumorigenesis and colon cancer growth. PLoS One, 3, e2020.
|