Chromatin Regulator | Alias | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KAT5 | TIP; ESA1; PLIP; TIP60; cPLA2; HTATIP; HTATIP1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
External Links: | Wiki GeneCards NCBI UniProt | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Related histone modifications: | H2AK5ac;H3K14ac;H4K5ac;H4K8ac;H4K12ac;H4K16ac | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Introduction | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Full Name: K(lysine) acetyltransferase 5 KAT5(also known as TIP60) is a histone acetyltransferase belonging to the MYST(MOZ, Ybf2/Sas3, Sas2, and TIP60) family, which could acetylate histone H2A, H3 and H4 in vitro, acting as both a transcriptional activator and a repressor, involved in cell differentiation, DNA damage responses, apoptosis(1-4,7-10,13-15). | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Function and Interaction | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| TIP60 is suggested to interact with Tat, thus participating in the modulation of HIV(human immunodeficiency virus) gene expression(1). TIP60 is shown to be a nuclear receptor coactivator, for it binds to the nuclear receptor(such as estrogen, androgen and progesterone receptors)in a ligand-dependent manner, thus involved in their transcriptional regulation(3-5). TIP60 is indicated to interact with p53, which is essential for the p21 promoter activation, it could also interfere the degradation of p53 under normal growth conditions(6).It could interact with MyoD, thus regulating the myoblast differentiation(7). TIP60 is a regulator of c-MYC and c-Myb as well(11,12). Studies have shown that TIP60 could perform its suppression through association with zinc finger E box-binding protein(ZEB), p73, cAMP response element binding protein and recruitment of histone deacetylases (HDACs)(13-15). TIP60 is identified to form a complex with p400, playing a role in maintaining embryonic stem cell identity(16). | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Disease Association | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| TIP60 is presented to be associated with human lymphomas and head-and-neck and mammary carcinomas(17). | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
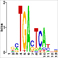
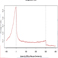
ChIP-Seq data
ChIP-Seq data of related histone modifications
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Notice: For bigwiggle or bed file download, if the browser cannot automatically download the file, users can right click the hyperlink and then click the "Save link as..." button, which will automatically redirect to download dialogue box, or click the "Copy link address" button and access the website in a new tab page. For data analysis in Cistrome, users should first login into the Cistrome website, then press the "Send Bed" or "Send Big wiggle" button. For data download by Cistrome, users can follow this tutorial. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
References | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1.Kamine J et al.(1996).Identification of a cellular protein that specifically interacts with the essential cysteine region of the HIV-1 Tat transactivator. Virology. 216(2):357-66. 2.Sapountzi V et al.(2006).Cellular functions of TIP60.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 38(9):1496-509. 3.Brady ME et al.(1999).Tip60 is a nuclear hormone receptor coactivator. J Biol Chem. 274(25):17599-604. 4.Halkidou K et al.(2003).Expression of Tip60, an androgen receptor coactivator, and its role in prostate cancer development. Oncogene. 22(16):2466-77. 5.Jeong KW et al.(2011).Recognition of enhancer element-specific histone methylation by TIP60 in transcriptional activation. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 18(12):1358-65. 6.Legube G et al.(2004).Role of the histone acetyl transferase Tip60 in the p53 pathway. J Biol Chem. 279(43):44825-33. 7.Kim JW et al.(2011). Tip60 regulates myoblast differentiation by enhancing the transcriptional activity of MyoD via their physical interactions. FEBS J. 278(22):4394-404. 8.Kimura A et al.(1998).Tip60 acetylates six lysines of a specific class in core histones in vitro. Genes Cells. 3(12):789-800. 9.Yamamoto T et al.(1997).Novel substrate specificity of the histone acetyltransferase activity of HIV-1-Tat interactive protein Tip60. J Biol Chem. 272(49):30595-8. 10.Ikura T et al.(2000).Involvement of the TIP60 histone acetylase complex in DNA repair and apoptosis. Cell. 102(4):463-73. 11.Patel JH et al.(2004).The c-MYC oncoprotein is a substrate of the acetyltransferases hGCN5/PCAF and TIP60. Mol Cell Biol. 24(24):10826-34. 12.Zhao H et al.(2012).The histone acetyltransferase TIP60 interacts with c-Myb and inactivates its transcriptional activity in human leukemia. J Biol Chem. 287(2):925-34. 13.Xiao H et al.(2003).Tip60 is a co-repressor for STAT3. J Biol Chem. 278(13):11197-204. 14.Gavaravarapu S et al.(2000).Tip60 inhibits activation of CREB protein by protein kinase A. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 269(3):758-66. 15. Kim JW et al.(2008).TIP60 represses transcriptional activity of p73beta via an MDM2-bridged ternary complex. J Biol Chem. 283(29):20077-86. 16.Fazzio TG et al.(2008). An RNAi screen of chromatin proteins identifies Tip60-p400 as a regulator of embryonic stem cell identity. Cell. 134(1):162-74. 17.Gorrini C et al.(2007).Tip60 is a haplo-insufficient tumour suppressor required for an oncogene-induced DNA damage response. Nature. 448(7157):1063-7. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Figure Gallery



About Chromatin Regulator
Chromatin Regulator Cistrome
is a unique database integrating curated information of CRs, CR ChIP-seq datasets, CR related HM ChIP-seq datasets, and analysis of the relationship between CRs and HMs ChIP-seq pairs in human and mouse.