Chromatin Regulator | Alias | |||||||||||||||||||
| SMARCC2 | Rsc8; BAF170; CRACC2 | |||||||||||||||||||
External Links: | Wiki GeneCards NCBI UniProt | |||||||||||||||||||
Related histone modifications: | NA | |||||||||||||||||||
Introduction | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Full name: SWI/SNF-related, matrix-associated, actin-dependent regulator of chromatin, subfamily c, member 2 . SMARCC2 is a chromatin remodeler and a subunit of the SWI/SNF complex, which requires hydrolysis of ATP to alter chromosome structure to regulate gene expression. Therefore, SMARCC2 plays a vital role in early embryonic development, differentiation, cell cycle modification, and the development of thymic T cells as well as tumors (1-4). | ||||||||||||||||||||
Function and Interaction | ||||||||||||||||||||
| BAF170 is a subunit of both the SWI/SNF complex and the related EKLF coactivator-remodeling complex 1 (E-RC1), similar to BAF155, which assists Erythroid KrŸppel-like factor (EKLF) in modulating human beta-globin expression (5). Together with BAF155, BAF170 can limit the protein levels of BAF57, which is an important mediator (6). BAF170 interacts with Smad2 and Smad3, which are transcriptional regulators that are activated by transforming growth factor (TGF) cytokines (7). | ||||||||||||||||||||
Disease Association | ||||||||||||||||||||
| BAF170 knockout can completely abolish the interaction between SWI/SNF and BRIT1, a BRCT-repeat inhibitor of hTERT expression, whose loss can cause primary microcephaly (8). BAF170 has been found to be dramatically modulated in cells following HIV-1 (human immunodeficiency virus type 1) transfection (9). | ||||||||||||||||||||
ChIP-Seq data
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Notice: For bigwiggle or bed file download, if the browser cannot automatically download the file, users can right click the hyperlink and then click the "Save link as..." button, which will automatically redirect to download dialogue box, or click the "Copy link address" button and access the website in a new tab page. For data analysis in Cistrome, users should first login into the Cistrome website, then press the "Send Bed" or "Send Big wiggle" button. For data download by Cistrome, users can follow this tutorial. | ||||||||||||||||||||
References | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 1. Muchardt, C. and Yaniv, M. (1999) ATP-dependent chromatin remodelling: SWI/SNF and Co. are on the job. J Mol Biol, 293, 187-198. 2. Kingston, R.E. and Narlikar, G.J. (1999) ATP-dependent remodeling and acetylation as regulators of chromatin fluidity. Gene Dev, 13, 2339-2352. 3. Bultman, S., Gebuhr, T., Yee, D., La Mantia, C., Nicholson, J., Gilliam, A., Randazzo, F., Metzger, D., Chambon, P., Crabtree, G. et al. (2000) A Brg1 null mutation in the mouse reveals functional differences among mammalian SWI/SNF complexes. Mol Cell, 6, 1287-1295. 4. Ahn, J., Ko, M., Lee, C., Kim, J., Yoon, H. and Seong, R.H. (2011) Srg3, a mouse homolog of BAF155, is a novel p53 target and acts as a tumor suppressor by modulating p21(WAF1/CIP1) expression. Oncogene, 30, 445-456. 5. Armstrong, J.A., Bieker, J.J. and Emerson, B.M. (1998) A SWI/SNF-related chromatin remodeling complex, E-RC1, is required for tissue-specific transcriptional regulation by EKLF in vitro. Cell, 95, 93-104. 6. Chen, J.G. and Archer, T.K. (2005) Regulating SWI/SNF subunit levels via protein-protein interactions and proteasomal degradation: BAF155 and BAF170 limit expression of BAF57. Mol Cell Biol, 25, 9016-9027. 7. Xi, Q.R., He, W., Zhang, X.H.F., Le, H.V. and Massague, J. (2008) Genome-wide impact of the BRG1 SWI/SNF chromatin remodeler on the transforming growth factor beta transcriptional program. J Biol Chem, 283, 1146-1155. 8. Peng, G., Yim, E.K., Dai, H., Jackson, A.P., van der Burgt, I., Pan, M.R., Hu, R.Z., Li, K.Y. and Lin, S.Y. (2009) BRIT1/MCPH1 links chromatin remodelling to DNA damage response. Nat Cell Biol, 11, 865-U221. 9. Van Duyne, R., Guendel, I., Narayanan, A., Gregg, E., Shafagati, N., Tyagi, M., Easley, R., Klase, Z., Nekhai, S., Kehn-Hall, K. et al. (2011) Varying Modulation of HIV-1 LTR Activity by BAF Complexes. J Mol Biol, 411, 581-596. | ||||||||||||||||||||
Figure Gallery
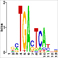


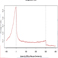
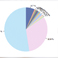

About Chromatin Regulator
Chromatin Regulator Cistrome
is a unique database integrating curated information of CRs, CR ChIP-seq datasets, CR related HM ChIP-seq datasets, and analysis of the relationship between CRs and HMs ChIP-seq pairs in human and mouse.