Chromatin Regulator | Alias | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KDM4A | JMJD2; JHDM3A; JMJD2A | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
External Links: | Wiki GeneCards NCBI UniProt | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Related histone modifications: | H4K20me3;H3K36me3;H3K36me2;H3K9me3;H3K9me2;H3K4me3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Introduction | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Full Name: Lysine (K)-specific demethylase 4A . KDM4A is a member of the JmjC domain-containing family of histone demethylases (JHDMs). It contains JmjN and JmjC domains, a 350-amino-acid linker region, two plant homeodomains (PHD), and a double Tudor domain. It plays a role in determining lifespan and in male-specific sex regulation, AR and heterochromatin modulation, herpes virus replication, and disease progression (1-14). | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Function and Interaction | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KDM4A interacts with the androgen receptor (AR) through its catalytic domain or C-terminus, and KDM4A overexpression can result in increasing AR transcription. Conversely, its knockdown can lead to decreased AR target gene transcription levels in LNCaP cells (5). KDM4A associates with heterochromatin protein 1a (HP1a) via the HP1-binding motif PxVxL, and its demethylation activity can be promoted by HP1a in Drosophila melanogaster (6). KDM4A is essential for the transcriptional regulation of genes associated with lifespan modulation, male-specific sex determination and courtship behavior, as studies have shown that disturbing KDM4A can decrease male lifespan and result in a male-specific wing extension/twitching phenotype in flies. KDM4A knockout can result in downregulation of the above-mentioned phenotype-associated genes, especially the longevity-associated heat shock protein 22 (Hsp22) gene and the fruitless gene (7-11), which is involved in male sex determination. Overexpression of KDM4A can enhance the reactivation of KaposiÕs sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV), and K-bZIP, which is encoded by KSHV, can suppress the demethylase activity of KDM4A (12). | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Disease Association | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KDM4A is considered a potential biomarker of the prognosis of bladder cancer, as underexpression of KDM4A is related to poor prognostic characteristics, such as lymphovascular invasion, concomitant carcinoma in situ, and tobacco use, and usually indicates poor overall survival (13). KDM4A causes cardiac hypertrophy under hypertrophic stimuli and is overexpressed in human hypertrophic cardiomyopathy patients (14). | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
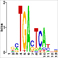
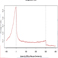
ChIP-Seq data
ChIP-Seq data of related histone modifications
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Notice: For bigwiggle or bed file download, if the browser cannot automatically download the file, users can right click the hyperlink and then click the "Save link as..." button, which will automatically redirect to download dialogue box, or click the "Copy link address" button and access the website in a new tab page. For data analysis in Cistrome, users should first login into the Cistrome website, then press the "Send Bed" or "Send Big wiggle" button. For data download by Cistrome, users can follow this tutorial. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
References | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1. Couture, J.F., Collazo, E., Ortiz-Tello, P.A., Brunzelle, J.S. and Trievel, R.C. (2007) Specificity and mechanism of JMJD2A, a trimethyllysine-specific histone demethylase. Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, 14, 689-695. 2. Chen, Z.Z., Zang, J.Y., Kappler, J., Hong, X., Crawford, F., Wang, Q., Lan, F., Jiang, C.Y., Whetstine, J., Dai, S. et al. (2007) Structural basis of the recognition of a methylated histone tail by JMJD2A. P Natl Acad Sci USA, 104, 10818-10823. 3. Lee, J., Thompson, J.R., Botuyan, M.V. and Mer, G. (2008) Distinct binding modes specify the recognition of methylated histones H3K4 and H4K20 by JMJD2A-tudor. Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, 15, 109-111. 4. Ng, S.S., Kavanagh, K.L., McDonough, M.A., Butler, D., Pilka, E.S., Lienard, B.M.R., Bray, J.E., Savitsky, P., Gileadi, O., von Delft, F. et al. (2007) Crystal structures of histone demethylase JMJD2A reveal basis for substrate specificity. Nature, 448, 87-91. 5. Shin, S. and Janknecht, R. (2007) Activation of androgen receptor by histone demethylases JMJD2A and JMJD2D. Biochem Bioph Res Co, 359, 742-746. 6. Lin, C.H., Li, B., Swanson, S., Zhang, Y., Florens, L., Washburn, M.P., Abmayr, S.M. and Workman, J.L. (2008) Heterochromatin Protein 1a Stimulates Histone H3 Lysine 36 Demethylation by the Drosophila KDM4A Demethylase. Mol Cell, 32, 696-706. 7. Dickson, B.J. (2002) Molecular mechanisms of axon guidance. Science, 298, 1959-1964. 8. Morrow, G., Battistini, S., Zhang, P. and Tanguay, R.M. (2004) Decreased lifespan in the absence of expression of the mitochondrial small heat shock protein Hsp22 in Drosophila. J Biol Chem, 279, 43382-43385. 9. Certel, S.J., Savella, M.G., Schlegel, D.C.F. and Kravitz, E.A. (2007) Modulation of Drosophila male behavioral choice. P Natl Acad Sci USA, 104, 4706-4711. 10. Dickson, B.J. (2008) Wired for Sex: The Neurobiology of Drosophila Mating Decisions. Science, 322, 904-909. 11. Lorbeck, M.T., Singh, N., Zervos, A., Dhatta, M., Lapchenko, M., Yang, C. and Elefant, F. (2010) The histone demethylase DmelKdm4A controls genes required for life span and male-specific sex determination in Drosophila. Gene, 450, 8-17. 12. Chang, P.C., Fitzgerald, L.D., Hsia, D.A., Izumiya, Y., Wu, C.Y., Hsieh, W.P., Lin, S.F., Campbell, M., Lam, K.S., Luciw, P.A. et al. (2011) Histone Demethylase JMJD2A Regulates Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Replication and Is Targeted by a Viral Transcriptional Factor. J Virol, 85, 3283-3293. 13. Kauffman, E.C., Robinson, B.D., Downes, M.J., Powell, L.G., Lee, M.M., Scherr, D.S., Gudas, L.J. and Mongan, N.P. (2011) Role of Androgen Receptor and Associated Lysine-Demethylase Coregulators, LSD1 and JMJD2A, in Localized and Advanced Human Bladder Cancer. Mol Carcinogen, 50, 931-944. 14. Zhang, Q.J., Chen, H.Z., Wang, L., Liu, D.P., Hill, J.A. and Liu, Z.P. (2011) The histone trimethyllysine demethylase JMJD2A promotes cardiac hypertrophy in response to hypertrophic stimuli in mice. J Clin Invest, 121, 2447-2456. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Figure Gallery



About Chromatin Regulator
Chromatin Regulator Cistrome
is a unique database integrating curated information of CRs, CR ChIP-seq datasets, CR related HM ChIP-seq datasets, and analysis of the relationship between CRs and HMs ChIP-seq pairs in human and mouse.