Chromatin Regulator | Alias | |||||||||||||||||||
| RAC3 | ACTR; AIB1; NCOA3; SRC3; pCIP; AIB-1; CTG26; SRC-3; CAGH16; KAT13B; TNRC14; TNRC16; TRAM-1; bHLHe42 | |||||||||||||||||||
External Links: | Wiki GeneCards NCBI UniProt | |||||||||||||||||||
Related histone modifications: | NA | |||||||||||||||||||
Introduction | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Full Name: Ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 3 (rho family, small GTP binding protein Rac3) . RAC3 is a member of the Rac GTPases within the Rho family. This gene is located in the chromosome 17q23-25 region, which is frequently deleted in breast cancers. RAC3 is specifically expressed in the nervous system, and its expression developmentally regulated. The GTPase activity of RAC3 can be promoted through its interaction with Bcr in vitro and may play a role in stress activation pathways, neuronal development, cognitive development, differentiation, cytoskeletal rearrangement, transcriptional regulation, organ development, and autophagy (1-11). | ||||||||||||||||||||
Function and Interaction | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Although RAC3 knockout mice are viable and fertile, they show decreased behavioral flexibility in new situations, suggesting that RAC3 plays a role in normal cognitive development (1-2). RAC3 is coexpressed in neurons with another Rac GTPase, Rac1, and both GTPases are required during neuronal development. The simultaneous deletion of both of these genes can result in disruption of hippocampus development, behavioral motor defects, epilepsy, and premature death in mice as well as loss of immune competence and disruption of thymic and splenic development (3-4). RAC3 and RAC1 are thought to exhibit opposing functions in neuronal cells. RAC1 is associated with cell spreading and the promotion of neuritogenesis via stimulating PAK1 and enhancing the GIT1-paxillin interaction. In contrast, RAC3 tends to induce a contractile, round morphology and prevents neuronal differentiation by inhibiting the GIT1-paxillin interaction and suppressing Arf6 by inducing the GAP function of GIT1 (6-7). RAC3 is a putative ERalpha co-regulator and is essential for full ERalpha transcriptional activity. RAC3 suppression can result in reduced E2-induced cell proliferation, cell migration, and ERalpha-mediated gene expression (5). | ||||||||||||||||||||
Disease Association | ||||||||||||||||||||
| RAC3 is associated with Ph-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia, as its deletion can result in longer average survival (8). Overexpression of RAC3 stimulates pro-growth and pro-migratory genes, thus leading to increased migration of ERalpha-positive breast cancer cells, indicating RAC3 as a potential pharmaceutical target for the treatment of ERalpha-positive breast cancers (5). | ||||||||||||||||||||
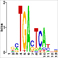
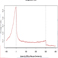
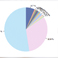
ChIP-Seq data
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Notice: For bigwiggle or bed file download, if the browser cannot automatically download the file, users can right click the hyperlink and then click the "Save link as..." button, which will automatically redirect to download dialogue box, or click the "Copy link address" button and access the website in a new tab page. For data analysis in Cistrome, users should first login into the Cistrome website, then press the "Send Bed" or "Send Big wiggle" button. For data download by Cistrome, users can follow this tutorial. | ||||||||||||||||||||
References | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 1. Corbetta, S., Gualdoni, S., Albertinazzi, C., Paris, S., Croci, L., Consalez, G.G. and de Curtis, I. (2005) Generation and characterization of Rac3 knockout mice. Mol Cell Biol, 25, 5763-5776. 2. Corbetta, S., D'Adarno, P., Gualdoni, S., Braschi, C., Berardi, N. and de Curtis, I. (2008) Hyperactivity and novelty-induced hyperreactivity in mice lacking Rac3. Behav Brain Res, 186, 246-255. 3. Corbetta, S., Gualdoni, S., Ciceri, G., Monari, M., Zuccaro, E., Tybulewicz, V.L.J. and de Curtis, I. (2009) Essential role of Rac1 and Rac3 GTPases in neuronal development. Faseb J, 23, 1347-1357. 4. Basso, V., Corbetta, S., Gualdoni, S., Tonoli, D., Poliani, P.L., Sanvito, F., Doglioni, C., Mondino, A. and de Curtis, I. (2011) Absence of Rac1 and Rac3 GTPases in the nervous system hinders thymic, splenic and immune-competence development. Eur J Immunol, 41, 1410-1419. 5. Walker, M.P., Zhang, M., Le, T.P., Wu, P., Laine, M. and Greene, G.L. (2011) RAC3 is a pro-migratory co-activator of ER alpha. Oncogene, 30, 1984-1994. 6. Hajdo-Milasinovic, A., Ellenbroek, S.I.J., van Es, S., van der Vaart, B. and Collard, J.G. (2007) Rac1 and Rac3 have opposing functions in cell adhesion and differentiation of neuronal cells. J Cell Sci, 120, 555-566. 7. Hajdo-Milasinovic, A., van der Kammen, R.A., Moneva, Z. and Collard, J.G. (2009) Rac3 inhibits adhesion and differentiation of neuronal cells by modifying GIT1 downstream signaling. J Cell Sci, 122, 2127-2136. 8. Cho, Y.J., Zhang, B., Kaartinen, V., Haataja, L., de Curtis, I., Groffen, J. and Heisterkamp, N. (2005) Generation of rac3 null mutant mice: Role of Rac3 in Bcr/Abl-caused lymphoblastic leukemia. Mol Cell Biol, 25, 5777-5785. 9. Haataja, L., Groffen, J. and Heisterkamp, N. (1997) Characterization of RAC3, a novel member of the Rho family. J Biol Chem, 272, 20384-20388. 10. Malosio, M.L., Gilardelli, D., Paris, S., Albertinazzi, C. and deCurtis, I. (1997) Differential expression of distinct members of Rho family GTP-binding proteins during neuronal development: Identification of Rac1B, a new neural-specific member of the family. J Neurosci, 17, 6717-6728. 11. Zhu, W.L., Hossain, M.S., Guo, D.Y., Liu, S., Tong, H.L., Khakpoor, A., Casey, P.J. and Wang, M. (2011) A Role for Rac3 GTPase in the Regulation of Autophagy. J Biol Chem, 286, 35291-35298. | ||||||||||||||||||||
Figure Gallery



About Chromatin Regulator
Chromatin Regulator Cistrome
is a unique database integrating curated information of CRs, CR ChIP-seq datasets, CR related HM ChIP-seq datasets, and analysis of the relationship between CRs and HMs ChIP-seq pairs in human and mouse.