Chromatin Regulator | Alias | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| TDRD3 | Tudor Domain Containing 3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
External Links: | Wiki GeneCards NCBI UniProt | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Related histone modifications: | H3R17me2a;H4R3me2a | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Introduction | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Full name: Tudor Domain Containing 3. TDRD3 is an effector molecule for arginine-methylated histone marks on histone tails.It contains a Tudor domain and a UBA domain,the Tudor domain specifically recognizes and binds asymmetric dimethylation of histone H3R17(H3R17me2a) and histone H4R3(H4R3me2a),2 tags for epigenetic transcriptional activation.In cytoplasm,it may play a role in the assembly and/or disassembly of mRNA stress granules of transition of target mRNAs by binding Arg/Gly-rich motifs(GAR) in dimethylarginine-containing proteins(1-7). | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Function and Interaction | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| TDRD3 is an effector molecule that promotes transcription by binding methylarginine marks on histone tails,and it is a transcriptional coactivator requires its intact Tudor domain(1).It has also been reported that TDRD3 localizes predominantly to the cytoplasm,where it co-sediments with the fragile X mental retardation protein on actively translating polyribosomes and TDRD3 accumulates into stress granules(SGs) in response to various cellular stresses(2,5).TDRD3 may play a role in the regulation of translation of target mRNAs by binding Arg/Gly-rich motifs(GAR) in dimethylarginine-containing proteins(3). | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Disease Association | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| TDRD3 co-sediments with the fragile X mental retardation protein on actively translating polyribosomes,and it is overexpressed in estrogen-negative breast cancers(2,5). | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
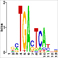
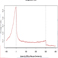
ChIP-Seq data
ChIP-Seq data of related histone modifications
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Notice: For bigwiggle or bed file download, if the browser cannot automatically download the file, users can right click the hyperlink and then click the "Save link as..." button, which will automatically redirect to download dialogue box, or click the "Copy link address" button and access the website in a new tab page. For data analysis in Cistrome, users should first login into the Cistrome website, then press the "Send Bed" or "Send Big wiggle" button. For data download by Cistrome, users can follow this tutorial. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
References | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1.Yang, Y., Lu, Y., Espejo, A., Wu, J., Xu, W., Liang, S., and Bedford, M.T. (2010). TDRD3 is an effector molecule for arginine-methylated histone marks. Mol Cell 40, 1016-1023. 2.Goulet, I., Boisvenue, S., Mokas, S., Mazroui, R., and Cote, J. (2008). TDRD3, a novel Tudor domain-containing protein, localizes to cytoplasmic stress granules. Hum Mol Genet 17, 3055-3074. 3.Cote, J., and Richard, S. (2005). Tudor domains bind symmetrical dimethylated arginines. J Biol Chem 280, 28476-28483. 4.Hurley, J.H., Lee, S., and Prag, G. (2006). Ubiquitin-binding domains. Biochem J 399, 361-372. 5.Linder, B., Plottner, O., Kroiss, M., Hartmann, E., Laggerbauer, B., Meister, G., Keidel, E., and Fischer, U. (2008). Tdrd3 is a novel stress granule-associated protein interacting with the Fragile-X syndrome protein FMRP. Hum Mol Genet 17, 3236-3246. 6.Kashima, I., Jonas, S., Jayachandran, U., Buchwald, G., Conti, E., Lupas, A.N., and Izaurralde, E. (2010). SMG6 interacts with the exon junction complex via two conserved EJC-binding motifs (EBMs) required for nonsense-mediated mRNA decay. Genes Dev 24, 2440-2450. 7.Zhao, D.Y., Gish, G., Braunschweig, U., Li, Y., Ni, Z., Schmitges, F.W., Zhong, G., Liu, K., Li, W., Moffat, J., et al. (2016). SMN and symmetric arginine dimethylation of RNA polymerase II C-terminal domain control termination. Nature 529, 48-53. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Figure Gallery



About Chromatin Regulator
Chromatin Regulator Cistrome
is a unique database integrating curated information of CRs, CR ChIP-seq datasets, CR related HM ChIP-seq datasets, and analysis of the relationship between CRs and HMs ChIP-seq pairs in human and mouse.