Chromatin Regulator | Alias |
| HDAC2 | HD2; RPD3; YAF1 |
External Links: | Wiki GeneCards NCBI UniProt |
Related histone modifications: | H2AK5ac;H3K4ac;H3K14ac;H3K27ac;H3K56ac;H4K5ac;H4K8ac;H4K12ac;H4K16ac |
Introduction | |
| Full Name: Histone deacetylase 2
.
HDAC2 is a zinc-dependent class I histone deacetylase. It possesses a highly conserved deacetylase domain and is closely related to HDAC1. HDAC2 coexists in the CoREST, NuRD, and Sin3 complexes and often exhibits redundant functions with HDAC1 during later development. Additionally, HDAC2 is overexpressed in many cancers and is involved in transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, the DNA damage response, development, and organogenesis (1-11).
|
Function and Interaction | |
| HDAC2 suppression increases p21 expression and apoptosis, leading to a decreased cell density (1). The HDAC1/HDAC2 dimer interacts with EZH2, assisting EZH2 in its interaction with Snail, thus forming the EZH2/HDAC1/ HDAC 2/Snail complex, which may be related to the progression of nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) (2). HDAC2 is directly ubiquitinated and degraded by Mule (Mcl-1 ubiquitin ligase E3), and Mule-HDAC2 is believed to alter p53 activity. Thus, HDAC2 is associated with the p53 pathway and DNA damage response and could also be related to gene expression and apoptosis through pathways not involving p53 (3). In addition to p53, HDAC2 suppresses p63 during epidermal development (4). Highly HDAC2 expression disrupts memory formation and synaptic maturation and can inhibit neuronal gene expression as well (5-6). HDAC2 is more abundant in neurons than HDAC1 and can be modified by S-nitrosylation, thus promoting chromatin remodeling and modulating EGR1 expression, dendritic growth, and branching in neurons (5,7). HDAC2 is related to organogenesis, specifically being involved in myocardial growth, morphogenesis, and contractility (8).
|
Disease Association | |
| High levels of HDAC2 expression are associated with tumor cell proliferation, and HDAC2 has been shown to be overexpressed in renal cell, prostate, gastric, and esophageal cancers (12-15). HDAC2 overexpression is also found in oral cancer and is suggested to be a prognostic factor in oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) (16). HDAC2 is mutated in colon cancer, indicating this protein as a potential pharmacogenetic target for cancer treatment (17).
|
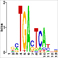
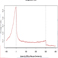
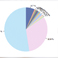
ChIP-Seq data
ChIP-Seq data of related histone modifications
|
| Notice: For bigwiggle or bed file download, if the browser cannot automatically download the file,
users can right click the hyperlink and then click the "Save link as..." button, which will automatically redirect to download dialogue box, or click the "Copy link address" button
and access the website in a new tab page. For data analysis in Cistrome, users should first login into the Cistrome website,
then press the "Send Bed" or "Send Big wiggle" button. For data download by Cistrome, users can follow this tutorial.
|
References | |
1. Huang, B.H., Laban, M., Leung, C.H.W., Lee, L., Lee, C.K., Salto-Tellez, M., Raju, G.C. and Hooi, S.C. (2005) Inhibition of histone deacetylase 2 increases apoptosis and p21(Cip1/WAF1) expression, independent of histone deacetylase 1. Cell Death Differ, 12, 395-404.
2. Tong, Z.T., Cai, M.Y., Wang, X.G., Kong, L.L., Mai, S.J., Liu, Y.H., Zhang, H.B., Liao, Y.J., Zheng, F., Zhu, W. et al. (2012) EZH2 supports nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell aggressiveness by forming a co-repressor complex with HDAC1/HDAC2 and Snail to inhibit E-cadherin. Oncogene, 31, 583-594.
3. Zhang, J., Kan, S., Huang, B., Hao, Z.Y., Mak, T.W. and Zhong, Q. (2011) Mule determines the apoptotic response to HDAC inhibitors by targeted ubiquitination and destruction of HDAC2. Gene Dev, 25, 2610-2618.
4. LeBoeuf, M., Terrell, A., Trivedi, S., Sinha, S., Epstein, J.A., Olson, E.N., Morrisey, E.E. and Millar, S.E. (2010) Hdac1 and Hdac2 Act Redundantly to Control p63 and p53 Functions in Epidermal Progenitor Cells. Dev Cell, 19, 807-818.
5. Guan, J.S., Haggarty, S.J., Giacometti, E., Dannenberg, J.H., Joseph, N., Gao, J., Nieland, T.J.F., Zhou, Y., Wang, X.Y., Mazitschek, R. et al. (2009) HDAC2 negatively regulates memory formation and synaptic plasticity. Nature, 459, 55-U58.
6. Akhtar, M.W., Raingo, J., Nelson, E.D., Montgomery, R.L., Olson, E.N., Kavalali, E.T. and Monteggia, L.M. (2009) Histone Deacetylases 1 and 2 Form a Developmental Switch That Controls Excitatory Synapse Maturation and Function. J Neurosci, 29, 8288-8297.
7. Nott, A., Watson, P.M., Robinson, J.D., Crepaldi, L. and Riccio, A. (2008) S-nitrosylation of histone deacetylase 2 induces chromatin remodelling in neurons. Nature, 455, 411-U467.
8. Montgomery, R.L., Davis, C.A., Potthoff, M.J., Haberland, M., Fielitz, J., Qi, X.X., Hill, J.A., Richardson, J.A. and Olson, E.N. (2007) Histone deacetylases 1 and 2 redundantly regulate cardiac morphogenesis, growth, and contractility. Gene Dev, 21, 1790-1802.
9. Yang, X.J. and Seto, E. (2008) The Rpd3/Hda1 family of lysine deacetylases: from bacteria and yeast to mice and men. Nat Rev Mol Cell Bio, 9, 206-218.
10. Spiegel, S., Milstien, S. and Grant, S. (2012) Endogenous modulators and pharmacological inhibitors of histone deacetylases in cancer therapy. Oncogene, 31, 537-551.
11. Hassig, C.A., Tong, J.K., Fleischer, T.C., Owa, T., Grable, P.G., Ayer, D.E. and Schreiber, S.L. (1998) A role for histone deacetylase activity in HDAC1-mediated transcriptional repression. P Natl Acad Sci USA, 95, 3519-3524.
12. Fritzsche, F.R., Weichert, W., Roske, A., Gekeler, V., Beckers, T., Stephan, C., Jung, K., Scholman, K., Denkert, C., Dietel, M. et al. (2008) Class I histone deacetylases 1, 2 and 3 are highly expressed in renal cell cancer. Bmc Cancer, 8.
13. Weichert, W., Roske, A., Gekeler, V., Beckers, T., Stephan, C., Jung, K., Fritzsche, F.R., Niesporek, S., Denkert, C., Dietel, M. et al. (2008) Histone deacetylases 1, 2 and 3 are highly expressed in prostate cancer and HDAC2 expression is associated with shorter PSA relapse time after radical prostatectomy. Brit J Cancer, 98, 604-610.
14. Mutze, K., Langer, R., Becker, K., Ott, K., Novotny, A., Luber, B., Hapfelmeier, A., Gottlicher, M., Hofler, H. and Keller, G. (2010) Histone Deacetylase (HDAC) 1 and 2 Expression and Chemotherapy in Gastric Cancer. Ann Surg Oncol, 17, 3336-3343.
15. Langer, R., Mutze, K., Becker, K., Feith, M., Ott, K., Hofler, H. and Keller, G. (2010) Expression of class I histone deacetylases (HDAC1 and HDAC2) in oesophageal adenocarcinomas: an immunohistochemical study. J Clin Pathol, 63, 994-998.
16. Chang, H.H., Chiang, C.P., Hung, H.C., Lin, C.Y., Deng, Y.T. and Kuo, M.Y.P. (2009) Histone deacetylase 2 expression predicts poorer prognosis in oral cancer patients. Oral Oncol, 45, 610-614.
17. Ropero, S., Fraga, M.F., Ballestar, E., Hamelin, R., Yamamoto, H., Boix-Chornet, M., Caballero, R., Alaminos, M., Setien, F., Paz, M.F. et al. (2006) A truncating mutation of HDAC2 in human cancers confers resistance to histone deacetylase inhibition. Nat Genet, 38, 566-569.
|